
How It’s Made Peanut Butter Episode?
2025-09-08 by Sherry
Peanut butter is a popular food that has a large consumer base in the global market due to its unique aroma, delicate taste and rich nutritional value. So how It's made peanut butter episode?
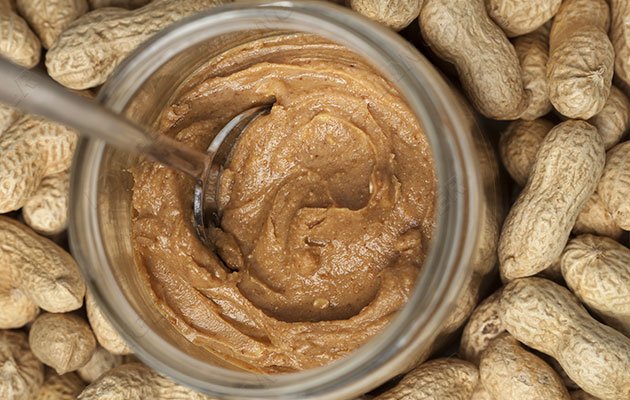

1. Raw Material Selection and Cleaning
The quality of peanut butter depends primarily on the raw peanuts. Factories typically select peanuts that are plump, mature, and free of mold as their primary raw material.
Sorting: Manual or automatic sorting removes impurities and foreign matter.
Cleaning: Peanut cleaning machines remove dirt, dust, and fine impurities from the peanuts to ensure hygienic processing.
2. Roasting
Roasting is a crucial step in peanut butter production.
The Maillard reaction occurs during the roasting process, enhancing the peanuts' flavor and color.
Factories typically use hot air ovens or drum roasters, typically controlling the temperature between 160°C and 180°C for 20 to 30 minutes, depending on the peanut variety and moisture content.
Roasted peanuts have a richer flavor and the skins are easier to peel.
3. Peeling and Sorting
After roasting, the peanuts need to be peeled.
A peeling machine removes the skins by friction or airflow.
During this process, a gravity sorter is used to remove unripe peanuts and broken kernels to ensure the taste and quality of the peanut butter.
3. Grinding
This is the core step in peanut butter production. Grinding is performed using a colloid mill, creating a fine peanut butter.
During the grinding process, the oils in the peanuts are gradually released, resulting in a smooth, fluid peanut butter.
4. Grinding
This is the core step in peanut butter production. Grinding is performed using a colloid mill, creating a fine peanut butter.
During the grinding process, the oils in the peanuts are gradually released, resulting in a smooth, fluid peanut butter.
5. Recipe Adjustment
To meet different market demands, peanut butter can be blended with appropriate ingredients.
Seasoning: Add salt, sugar, or honey to adjust the flavor.
Stabilizers and emulsifiers: Such as palm oil, vegetable oil, or lecithin, are used to prevent oil-water separation and maintain a stable peanut butter texture.
Granular peanut butter: Add some coarsely chopped peanuts to the fine peanut butter to enhance the texture.
6. Vacuum Degassing and Sterilization
Vacuum degassing: Removes air bubbles from peanut butter under a vacuum to prevent oxidation and microbial growth.
Sterilization: Pasteurization or high-temperature transient sterilization (HTST) is commonly used to ensure product safety and extend shelf life.
Peanut butter production follows a highly automated and standardized process, with strict control over every step, from raw material selection, baking, peeling, grinding, blending, sterilization, and packaging. This production method not only ensures the aroma and taste of peanut butter, but also ensures product safety and nutrition.

1. Raw Material Selection and Cleaning
The quality of peanut butter depends primarily on the raw peanuts. Factories typically select peanuts that are plump, mature, and free of mold as their primary raw material.
Sorting: Manual or automatic sorting removes impurities and foreign matter.
Cleaning: Peanut cleaning machines remove dirt, dust, and fine impurities from the peanuts to ensure hygienic processing.
2. Roasting
Roasting is a crucial step in peanut butter production.
The Maillard reaction occurs during the roasting process, enhancing the peanuts' flavor and color.
Factories typically use hot air ovens or drum roasters, typically controlling the temperature between 160°C and 180°C for 20 to 30 minutes, depending on the peanut variety and moisture content.
Roasted peanuts have a richer flavor and the skins are easier to peel.
3. Peeling and Sorting
After roasting, the peanuts need to be peeled.
A peeling machine removes the skins by friction or airflow.
During this process, a gravity sorter is used to remove unripe peanuts and broken kernels to ensure the taste and quality of the peanut butter.
3. Grinding
This is the core step in peanut butter production. Grinding is performed using a colloid mill, creating a fine peanut butter.
During the grinding process, the oils in the peanuts are gradually released, resulting in a smooth, fluid peanut butter.
4. Grinding
This is the core step in peanut butter production. Grinding is performed using a colloid mill, creating a fine peanut butter.
During the grinding process, the oils in the peanuts are gradually released, resulting in a smooth, fluid peanut butter.
5. Recipe Adjustment
To meet different market demands, peanut butter can be blended with appropriate ingredients.
Seasoning: Add salt, sugar, or honey to adjust the flavor.
Stabilizers and emulsifiers: Such as palm oil, vegetable oil, or lecithin, are used to prevent oil-water separation and maintain a stable peanut butter texture.
Granular peanut butter: Add some coarsely chopped peanuts to the fine peanut butter to enhance the texture.
6. Vacuum Degassing and Sterilization
Vacuum degassing: Removes air bubbles from peanut butter under a vacuum to prevent oxidation and microbial growth.
Sterilization: Pasteurization or high-temperature transient sterilization (HTST) is commonly used to ensure product safety and extend shelf life.
Peanut butter production follows a highly automated and standardized process, with strict control over every step, from raw material selection, baking, peeling, grinding, blending, sterilization, and packaging. This production method not only ensures the aroma and taste of peanut butter, but also ensures product safety and nutrition.
- Pre:Chicken Nuggets Frying Temperature
- Next:None




![[field:typename]](/templets/longer_zonghem/img/xj_blog.png) Case
Case![[field:typename]](/templets/longer_zonghem/img/xj_set.png) Service
Service![[field:typename]](/templets/longer_zonghem/img/xj_about.png) About
About Call
Call Message
Message